What Is a SEER Rating and What Does It Mean for Your HVAC System? (2024 Guide)
In this EcoWatch guide about SEER rating, you’ll learn:
- What is a SEER rating?
- What do the SEER numbers mean?
- What is a good SEER rating for an HVAC system?
- Why a SEER rating is important for an air conditioner?
Each product and or company featured here has been independently selected by the writer. You can learn more about our review methodology here. If you make a purchase using the links included, we may earn commission.
If you’re shopping for a new air conditioner, heat pump or any other cool air unit, you’ve probably been bombarded with tons of information. But there’s one thing homeowners need to focus on: The SEER rating.
The SEER tells you how energy-efficient your HVAC unit is. The higher the energy efficiency of your HVAC system, the higher the energy savings. As an environmental first publisher we understand the importance of SEER and will explain further what the SEER rating means and how to find the best HVAC system for your home.
If you’d like to skip the reading and get connected to HVAC professionals who are experts on the SEER system, click one of the links below to be connected with one of our providers.

Carrier Heating and Cooling
Pros
- Wide availability (25+ states)
- Focus on energy efficiency
- Transparent about environmental impact
- Industry-leading company
Cons
- Weak or non-existent warranty
- More expensive than some competitors

ARS Rescue Rooter
Pros
- Focus on energy efficiency
- Positive customer reviews
- 15+ years in business
- Outstanding social impact
- Strong warranty
- Offers eco-home systems (heat pumps, solar, etc)
- Financing options available
Cons
- Available in fewer than 25 states

Service Experts Heating
Pros
- Wide availability (25+ states)
- Positive customer reviews
- 15+ years in business
- Outstanding social impact
- Strong warranty
- Offers eco-home systems (heat pumps, solar, etc)
- Offers money-saving membership programs
Cons
- No emergency service
What Is a SEER Rating?
SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, although you may see it written as “Seasonal Energy Efficiency Rating” on one of your air conditioning systems or split systems.
The SEER number on your cooling system is directly tied to its unit’s energy efficiency. A higher SEER rating means a higher efficiency HVAC system, with some systems reaching up to 30 SEER for maximum efficiency. A high-efficiency system means your AC unit can perform better with less energy, therefore lowering household energy costs.
Other HVAC Acronyms
Without the “S,” EER stands for energy efficiency ratio, which measures the energy efficiency of your air conditioner or heat pump as it cools with an outdoor temperature of 95 degrees.
Another related acronym to know is HSPF, which stands for Heating Seasonal Performance Factor. HSPF is like SEER except it’s for heat, as it measures a heat pump’s overall energy efficiency throughout the heating season.
What Do the SEER Numbers Mean?
In simple terms, the SEER number measures how efficiently your air conditioner cools. To understand exactly how SEER is calculated, you should be aware of one more number: The unit’s total cooling output, which is expressed in British Thermal Units (BTUs).
SEER is calculated by the cooling output of the system over the typical cooling season, divided by the energy input over that same time period.

You can think of the SEER number similar to the miles per gallon of your car, with a higher SEER unit equating to a higher efficiency air conditioner. But just like miles per gallon, there are outside conditions that can alter the cooling efficiency at certain times.
What Is a Good SEER Rating for an HVAC System?
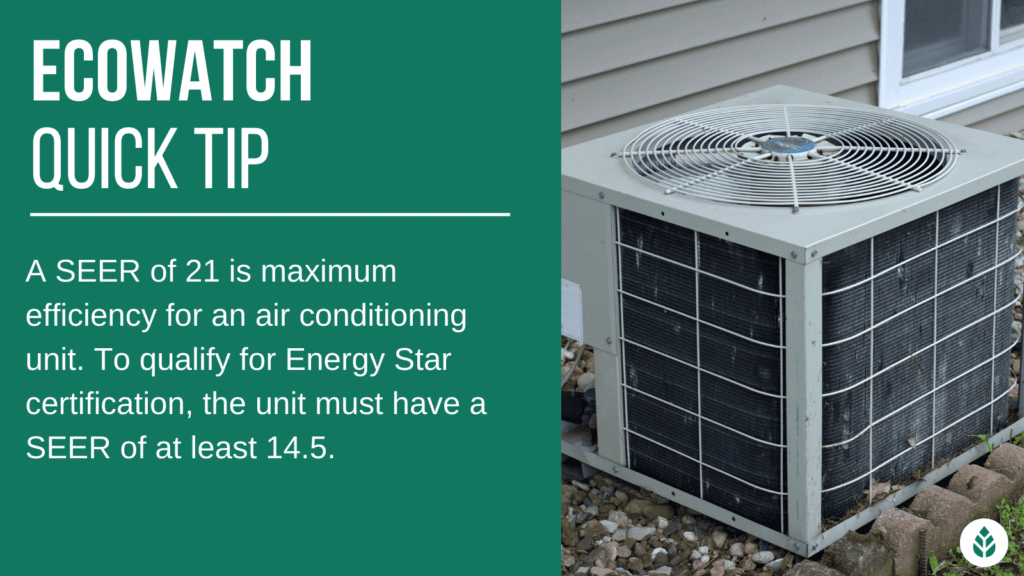
An air conditioner at 21 SEER is maximum efficiency. These days, most air conditioning units have a minimum SEER of 13. However, to qualify for an Energy Star certification, systems must have a SEER of at least 14.5.
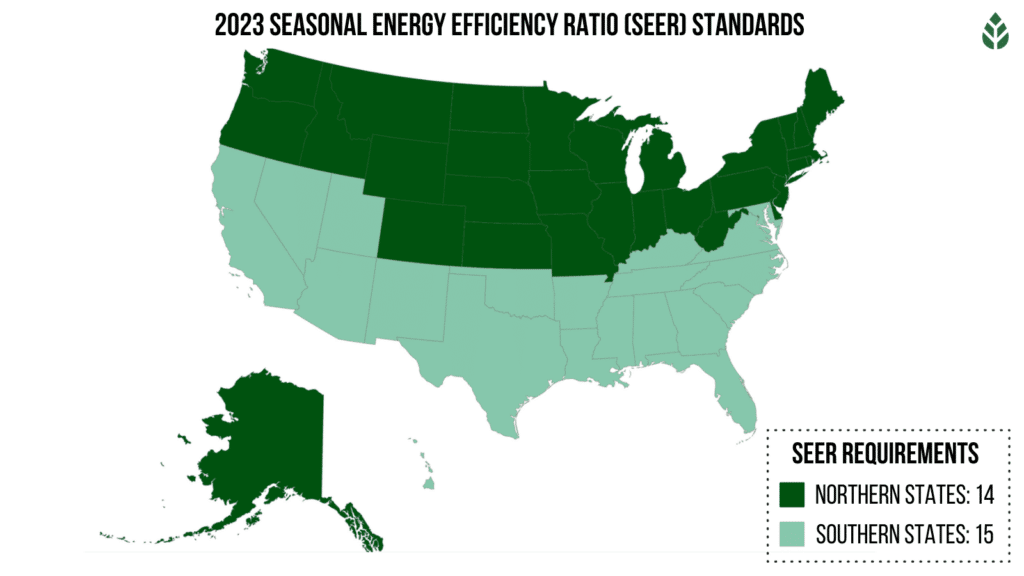
The U.S. Department of Energy has mandated efficiency standards for ductless and central air conditioners, but those ratings vary by region. The minimum standard for homes in the Northern U.S. was set at 13, but it has bumped up to a 14 SEER for 2024.
For homes in the Southern U.S. where outdoor temperatures are higher, the minimum SEER is moving from 14 to 15 starting in 2024.1
Why Is SEER Rating Important for an Air Conditioner?
The SEER rating is directly tied to the energy efficiency performance of an AC unit, whether that be a heat pump, a mini-split, or central air conditioning.
Systems with higher SEER may be more expensive, but higher energy efficiency means less energy consumption, which will lead to lower energy bills for your home.
Experts suggest that a 14 SEER air conditioner can pay for itself in electric energy savings in four years, although this is also dependent on having insulation and ductwork in good condition.
Fortunately, there are many tax incentives and rebates available for homeowners upgrading to more energy-efficient AC systems and heat pumps as well.
Outside of cost, choosing a higher SEER rating also lessens your impact on the environment. In the average size home, air conditioning consumes more than 2,000,000 watt-hours of electricity per year which requires power plants to emit 3,500 pounds of carbon dioxide and 31 pounds of sulfur dioxide.2
What Should You Look for In an Air Conditioning Unit?
Other than a high SEER rating, there are a few other features you should look for when buying an air conditioner.
- A lengthy warranty (the average lifespan of a central AC is 15 to 20 years)
- A variable speed system
- An automatic-delay fan switch to turn off the fan after the compressor turns off
- A unit that operates quietly
- A filter light to remind you to check the filter
FAQ: SEER Rating
The minimum standard SEER rating is 13, but an AC unit has to have a SEER of 14.5 to qualify for an Energy Star certification. If your unit is Energy Star certified, you can rest assured that it has a good SEER rating.
A unit with a higher SEER is going to cost more, but it will be worth it in energy savings. Experts suggest that an AC unit with a SEER of 13 or 14 can pay for itself in electric energy savings in four years, although this is also dependent on having insulation and ductwork in good condition.
Experts recommend investing in a unit with a SEER between 15 and 18 to get a good balance between money and performance. However, the ideal SEER for your home is dependent on climate and how much energy your system will need to cool your home. Starting in 2023, northern states will have a minimum SEER standard of 14, while southern states will have a minimum of 15.

 233k
233k  41k
41k  Subscribe
Subscribe